Driving Large Vehicles and Heavy Equipment
DOT Hazmat - General Awareness
DOT Hazmat - Highway Carrier Loading and Unloading Requirements
DOT Hazmat - Highway Carrier Segregation Requirements
DOT Hazmat - Security Requirements

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Alert Driving |
Understanding the importance of being an alert driver can mean the |
|
|
|
difference between life and death. Learn how to observe conditions |
|
|
|
around you, anticipate hazardous situations, and react to avoid hazards |
|
|
|
with our Alert Driving course. Our course discusses driving at safe speeds, |
|
|
|
the dangers of driving while impaired, and illustrates how to increase |
|
|
|
your reaction time by following the two-second rule. Alert driving is a |
|
|
|
fundamental element of safe, defensive driving techniques. |
|
|
|
At the end of this module, you will be able to: |
|
|
|
· Describe reasons why you should never drive while impaired |
|
|
|
· Describe how to scan the road |
|
|
|
· Identify things to look for while driving |
|
|
|
· Describe how to increase reaction time |
|
|
|
· Define the two-second rule |
|
|
|
· Define the speed limit |
|
|
Who can attend? |
|
|
|
Validation? |
Three years |
|
|
Certificate & ID |
Certificate & ID |
|
|
Exam |
Multi-choice exam |
|
|
Fee |
325 US$ + VAT |
|
|
More details |
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Work Zone Safety |
A work zone is an area of roadway associated with construction, |
|
|
|
maintenance, or utility work activities. Work zones are typically marked |
|
|
|
by signs, channeling devices, pavement markings, and/or work vehicles. |
|
|
|
Because they are often adjacent to active roadways, work zone workers |
|
|
|
are exposed to significant risks. Motorists, cyclists, and pedestrians can |
|
|
|
also face significant risks. Roadways and work activities differ, and |
|
|
|
weather, traffic volumes, and local environments also vary, so a "one size |
|
|
|
fits" all approach to work zone safety is not appropriate. However, there |
|
|
|
are policies, procedures, and guidelines which do apply to all. These are |
|
|
|
covered in this course. |
|
|
|
At the end of this module, you will be able to: |
|
|
|
· Define the term "work zone" |
|
|
|
· List hazardous conditions that work zones can present |
|
|
|
· Describe the components of a "Transportation Management |
|
|
|
Plan," which can include a "Temporary Traffic Control" plan, |
|
|
|
"Transportation Operations" plan, and "Public Information" plan |
|
|
|
· Describe the purpose and contents of the "Manual on Uniform |
|
|
|
Traffic Control Devices" |
|
|
|
· Identify and describe "positive protection devices," "exposure |
|
|
|
control measures," and "other traffic control measures" |
|
|
|
· Identify the four areas of a work zone |
|
|
|
· Describe the elements of an "Internal Traffic Control Plan" for a |
|
|
|
work zone |
|
|
|
· List safe behaviors to use when driving in or around work zones |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Who can attend? |
|
|
|
Validation? |
Three years |
|
|
Certificate & ID |
Certificate & ID |
|
|
Exam |
Multi-choice exam |
|
|
Fee |
325 US$ + VAT |
|
|
More details |
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DOT ERG Introduction |
The Department of Transportation's Emergency Response Guidebook |
|
|
|
(ERG) was created to help firefighters, law enforcement officers, medical |
|
|
|
personnel, and other first responders quickly identify the hazards present |
|
|
|
at transportation emergencies involving hazardous materials in order to |
|
|
|
protect themselves and the public. The ERG contains indexed lists of |
|
|
|
hazardous materials, the general hazards each material presents, and |
|
|
|
recommended safety precautions for emergency incidents. It is used in |
|
|
|
the U.S., Canada, Mexico, and several South American countries. |
|
|
|
At the end of this module, you will be able to: |
|
|
|
· Explain the purpose of the U.S. DOT's Emergency Response |
|
|
|
Guidebook (ERG) |
|
|
|
· Define the terms "hazardous material" and "initial response |
|
|
|
period" |
|
|
|
· Describe the purpose and contents of the six color-coded sections |
|
|
|
of the ERG |
|
|
Who can attend? |
|
|
|
Validation? |
Three years |
|
|
Certificate & ID |
Certificate & ID |
|
|
Exam |
Multi-choice exam |
|
|
Fee |
325 US$ + VAT |
|
|
More details |
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DOT HAZMAT Safety |
Over 4 billion tons of hazardous materials are transported in the U.S. |
|
|
|
every year. Due to their inherent risks to life, property, and the |
|
|
|
environment, the U.S. DOT established the Hazardous Materials |
|
|
|
Regulations (HMR) to cover the classification, labeling, packaging, and |
|
|
|
handling of hazardous materials. They also regulate hazmat training, |
|
|
|
incident reporting, hazard communication, and security. This course |
|
|
|
describes existing regulations for the transport of hazardous materials in |
|
|
|
commerce in the U.S., including the Hazardous Materials Table (HMT). |
|
|
|
t the end of this module, you will be able to: |
|
|
|
· Provide the U.S. Department of Transportation's (DOT) definitions |
|
|
|
for "hazardous material," "hazmat employer" and "hazmat |
|
|
|
employee" |
|
|
|
· Describe the key components of the U.S. DOT's Hazardous |
|
|
|
Materials Regulations (HMR) |
|
|
|
· Identify who must comply with the HMR |
|
|
|
· Use the information in the Hazardous Materials Table (HMT) from |
|
|
|
the HMR to correctly fill out the shipping description on a |
|
|
|
shipping document for a hazardous material |
|
|
|
· List the civil and criminal penalties that are possible for violations |
|
|
|
of the HMR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Who can attend? |
|
|
|
Validation? |
Three years |
|
|
Certificate & ID |
Certificate & ID |
|
|
Exam |
Multi-choice exam |
|
|
Fee |
325 US$ + VAT |
|
|
More details |
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Driving Hazard |
Safe drivers recognize potential hazards and stay out of harm's way. With |
|
|
Recognition |
our Driving Hazard Recognition course, you'll learn techniques for |
|
|
|
negotiating intersections and blind spots as well as avoiding erratic |
|
|
|
drivers, pedestrians, animals, and parked vehicles. You'll also learn about |
|
|
|
driving with limited visibility and in slippery conditions. Paying extra |
|
|
|
attention to common driving hazards can help ensure that your |
|
|
|
passengers and cargo return home safely. |
|
|
|
At the end of this module, you will be able to: |
|
|
|
Describe best driving practices in intersections |
|
|
|
Identify and describe blind spots |
|
|
|
Describe best driving practices during bad weather |
|
|
|
Describe best driving practices when obstacles are causing limited |
|
|
|
visibility |
|
|
|
Describe what to do when you begin to lose traction |
|
|
|
Explain how to deal with erratic drivers |
|
|
|
Describe best driving practices around pedestrian, animal, and parked |
|
|
|
vehicle hazards |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Who can attend? |
|
|
|
Validation? |
Three years |
|
|
Certificate & ID |
Certificate & ID |
|
|
Exam |
Multi-choice exam |
|
|
Fee |
325 US$ + VAT |
|
|
More details |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Driving Large Vehicles and Heavy Equipment

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Driving Large Vehicles |
Vehicles on public roadways come in many different shapes and sizes. |
|
|
and Heavy Equipment |
Most passenger vehicles - cars, vans, SUVs, and pickup trucks - have |
|
|
|
similar configurations and controls, and drivers of these vehicles |
|
|
|
understand their capabilities and limitations. However, drivers of large |
|
|
|
trucks and heavy equipment must use extra caution in order to safely |
|
|
|
navigate and share the roads with smaller vehicles. This course covers |
|
|
|
some of the things that must be considered when driving large vehicles or |
|
|
|
operating heavy equipment in order to ensure the safety of operators and |
|
|
|
people who are nearby. Topics covered include blind spot awareness, |
|
|
|
how to safely back up, dealing with inclement weather and poor road |
|
|
|
conditions, construction and work zone considerations, and minimizing in- |
|
|
|
cab distractions. |
|
|
|
At the end of this module, you will be able to: |
|
|
|
· List the items you should check before starting up a large vehicle |
|
|
|
or piece of heavy equipment |
|
|
|
· List the additional limitations that large vehicles and heavy |
|
|
|
equipment have when compared to smaller vehicles |
|
|
|
· Identify the blind spots on a large semi-truck |
|
|
|
· Describe how you can safely back up a large truck or piece of ….. |
|
|
Who can attend? |
|
|
|
Validation? |
Three years |
|
|
Certificate & ID |
Certificate & ID |
|
|
Exam |
Multi-choice exam |
|
|
Fee |
325 US$ + VAT |
|
|
More details |
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Load Securement |
Cargo Securement Standard provides the basis for the rules and |
|
|
|
regulations covering load securement on motor vehicles in the United |
|
|
|
States and Canada. This standard was created because unsecured loads |
|
|
|
can cause loss of life and load, cargo and vehicle damage, and accidents |
|
|
|
with other vehicles. This course covers the purpose of load securement, |
|
|
|
preparing loads, methods of load securement (including tie-down |
|
|
|
assemblies), working load limits, tie-down types, and safety. |
|
|
|
At the end of this module, you will be able to: |
|
|
|
· Specify where and when the North American Cargo Securement |
|
|
|
Standard applies |
|
|
|
· List the three methods of load securement on a motor vehicle |
|
|
|
· Define working load limit (WLL) and aggregate working load limit |
|
|
|
(AWLL) |
|
|
|
· Describe how the number of tie-downs required for a load is |
|
|
|
determined |
|
|
|
· List safety guidelines related to cargo securement |
|
|
|
· Identify when vehicles and load securement devices should be |
|
|
|
inspected during transport |
|
|
|
· List commodities which have special load securement |
|
|
|
requirements |
|
|
Who can attend? |
|
|
|
Validation? |
Three years |
|
|
Certificate & ID |
Certificate & ID |
|
|
Exam |
Multi-choice exam |
|
|
Fee |
325 US$ + VAT |
|
|
More details |
|
|
|
|
|
|
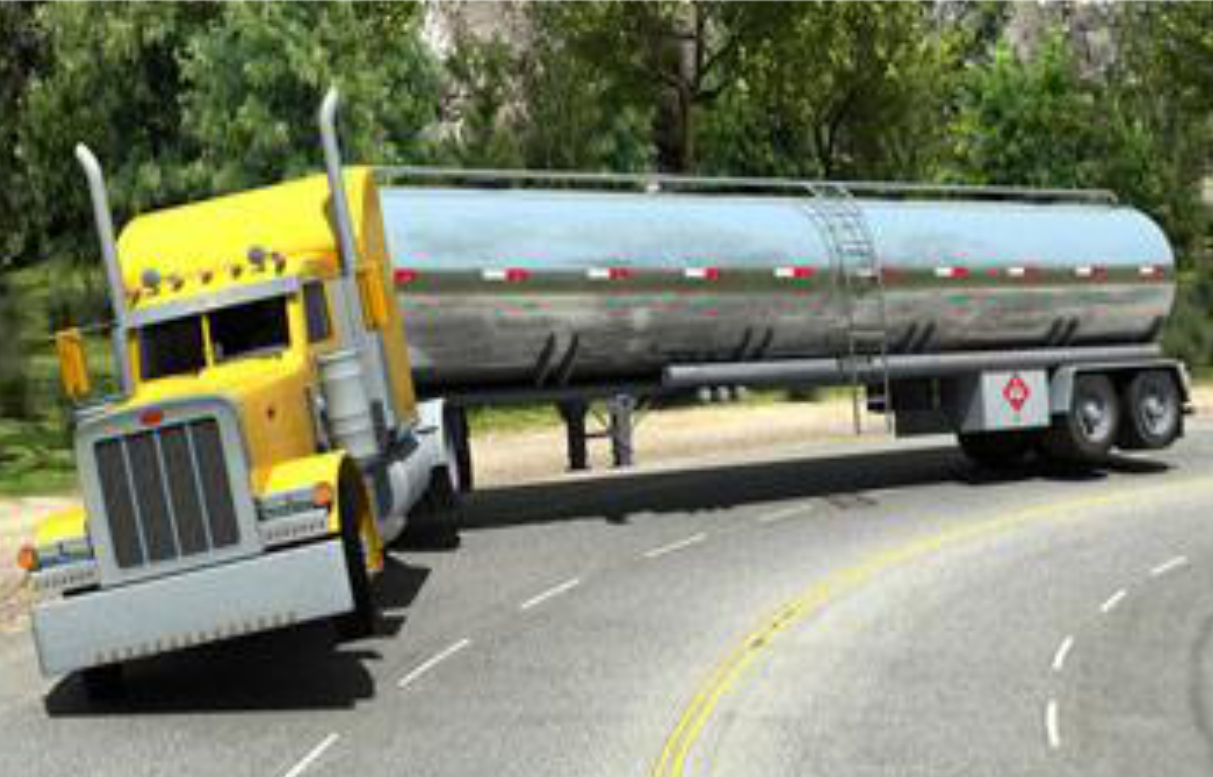

Tanker Rollover Approximately 1300 tanker truck rollovers occur every year. These
rollovers are the reason behind one in four accident-related truck driver
deaths. This course emphasizes the importance of drivers paying close
attention to the road and its conditions, as well as how their behaviors
and decisions can factor in a rollover.
At the end of this module, you will be able to:
|
|
· Describe what happens during a rollover |
|
|
|
· Identify four risk factors for rollovers |
|
|
|
· Identify how driver behavior can cause rollovers |
|
|
|
· Describe unsafe behaviors such as excessive speed |
|
|
|
· Describe how vehicle design can cause rollovers |
|
|
|
· Explain the impact of a high center of gravity |
|
|
|
· Describe load effects that can influence a rollover |
|
|
Who can attend? |
|
|
|
Validation? |
Three years |
|
|
Certificate & ID |
Certificate & ID |
|
|
Exam |
Multi-choice exam |
|
|
Fee |
325 US$ + VAT |
|
|
More details |
|
|
DOT Hazmat - General Awareness

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DOT Hazmat - General |
Regulations related to the transportation of hazardous materials are |
|
|
Awareness |
contained in Title 49 of the U.S. Code of Federal Regulations (CFR). The |
|
|
|
Hazardous Materials Regulations (HMR) in Parts 171-180 of Title 49 |
|
|
|
regulate the transportation of hazardous materials in commerce by motor |
|
|
|
vehicle, rail car, aircraft, or waterborne vessel. The HMR include |
|
|
|
classification, labeling, packaging, handling, loading and unloading |
|
|
|
requirements, in addition to standards for hazmat training, incident |
|
|
|
reporting, hazard communication, and security. |
|
|
|
At the end of this module, you will be able to: |
|
|
|
· Provide U.S. DOT definitions for "hazardous material," "hazmat |
|
|
|
employer" and "hazmat employee" |
|
|
|
· Identify the circumstances under which the U.S. DOT's Hazardous |
|
|
|
Materials Regulations (HMR) apply |
|
|
|
· Describe the responsibilities of hazmat employees and persons |
|
|
|
who offer hazardous materials for shipment |
|
|
|
· Use the Hazardous Materials Table to generate a basic description |
|
|
|
for use on shipping documents |
|
|
|
· Explain how hazardous substances, marine pollutants, elevated |
|
|
|
temperature materials, and hazardous wastes are identified and |
|
|
|
regulated during shipping |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Who can attend? |
|
|
|
Validation? |
Three years |
|
|
Certificate & ID |
Certificate & ID |
|
|
Exam |
Multi-choice exam |
|
|
Fee |
325 US$ + VAT |
|
|
More details |
|
|
|
|
|
|
DOT Hazmat - Highway Carrier Loading and Unloading Requirements

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DOT Hazmat - Highway |
The Hazardous Materials Regulations (HMR) apply to the transportation |
|
|
Carrier Loading and |
of hazardous materials in commerce. This includes the movement of |
|
|
Unloading |
these materials, plus all associated loading, unloading, and storage |
|
|
Requirements |
activities. Part 177 of the HMR contains requirements related to the |
|
|
|
transportation of hazardous materials by private, common, and contract |
|
|
|
"for hire" motor carriers. These carriers must also comply with several |
|
|
|
other Parts of the HMR, and many requirements of the Federal Motor |
|
|
|
Carrier Safety Regulations (FMCSR). |
|
|
|
At the end of this module, you will be able to: |
|
|
|
· Define the terms "hazardous material," "exclusive use," and "sole |
|
|
|
use," according to the Hazardous Materials Regulations (HMR) |
|
|
|
· Describe when the HMR apply to highway hazardous materials |
|
|
|
shipments |
|
|
|
· Describe the shipping paper recordkeeping requirements for |
|
|
|
hazmat carriers |
|
|
|
· List general loading and unloading requirements for hazardous |
|
|
|
materials |
|
|
|
· List the loading and unloading requirements for hazardous |
|
|
|
materials in Classes 1-5, 7, and 8 and Divisions 2.3 and 6.1 |
|
|
Who can attend? |
|
|
|
Validation? |
Three years |
|
|
Certificate & ID |
Certificate & ID |
|
|
Exam |
Multi-choice exam |
|
|
Fee |
325 US$ + VAT |
|
|
More details |
|
|
|
|
|
|
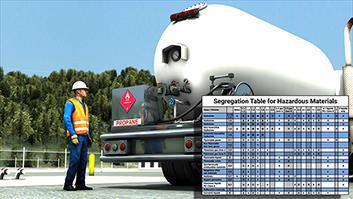
DOT Hazmat - Highway Carrier Segregation Requirements
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DOT Hazmat - Highway |
Certain hazardous materials must be separated from each other during |
|
|
Carrier Segregation |
transportation in a manner that prevents commingling if a package failure |
|
|
Requirements |
or leakage were to occur. The segregation requirements for highway |
|
|
|
hazmat shipments are contained in Section 177.848 of the HMR. These |
|
|
|
requirements apply only to the Hazard Classes and Divisions listed in the |
|
|
|
HMR's Segregation Table and only if the materials are in packages that |
|
|
|
require labeling or placarding, a compartment within a cargo tank, or a |
|
|
|
portable tank loaded in a container or vehicle. |
|
|
|
At the end of this module, you will be able to: |
|
|
|
Use the Segregation Table in Section 177.848 of the Hazardous |
|
|
|
Materials Regulations (HMR) to determine segregation requirements for |
|
|
|
commercial highway hazardous materials shipments |
|
|
|
Use the Compatibility Table to determine the segregation requirements |
|
|
|
for commercial highway shipments of Class 1 Explosives |
|
|
|
Determine when a transportation incident involving a hazardous |
|
|
|
material must be reported to the National Response Center (NRC) |
|
|
|
At the end of this module, you will be able to: |
|
|
|
· Use the Segregation Table in Section 177.848 of the Hazardous |
|
|
|
Materials Regulations (HMR) to determine segregation |
|
|
|
requirements for commercial highway hazardous materials |
|
|
|
shipments |
|
|
|
· Use the Compatibility Table to determine the segregation |
|
|
|
requirements for commercial highway shipments of Class 1 |
|
|
|
Explosives |
|
|
|
· Determine when a transportation incident involving a hazard……. |
|
|
Who can attend? |
|
|
|
Validation? |
Three years |
|
|
Certificate & ID |
Certificate & ID |
|
|
Exam |
Multi-choice exam |
|
|
Fee |
325 US$ + VAT |
|
|
More details |
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DOT Hazmat - Labeling |
The packaging used to secure hazardous materials during transport |
|
|
|
typically contains markings and labels to indicate that it contains a |
|
|
|
hazardous material. The purpose of marking and labeling is to |
|
|
|
communicate the hazards and risks of the materials being transported to |
|
|
|
anyone who could potentially be exposed to them."Labeling" refers to the |
|
|
|
placement of primary and, if applicable, subsidiary hazard labels on the |
|
|
|
outer package. DOT labeling requirements are contained in Part 172, |
|
|
|
Subpart E of the HMR. |
|
|
|
At the end of this module, you will be able to: |
|
|
|
· Define the terms hazardous material, packaging, package, bulk |
|
|
|
packaging, non-bulk packaging, marking, and labeling |
|
|
|
· Identify who is responsible for non-compliant hazardous material |
|
|
|
shipments |
|
|
|
· Use the Hazardous Materials Table and HMR to determine the |
|
|
|
required hazard labels for a package |
|
|
|
· List the international labels that can be used in place of or in |
|
|
|
addition to DOT hazmat labels |
|
|
|
· List durability, size, color, and placement requirements for DOT |
|
|
|
labels |
|
|
|
· Identify non-compliant hazmat packages |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Who can attend? |
|
|
|
Validation? |
Three years |
|
|
Certificate & ID |
Certificate & ID |
|
|
Exam |
Multi-choice exam |
|
|
Fee |
325 US$ + VAT |
|
|
More details |
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DOT Hazmat - Marking |
The packaging used to secure hazardous materials during transport |
|
|
|
typically contains markings and labels to indicate that it contains a |
|
|
|
hazardous material. The purpose of these markings and labels is to |
|
|
|
communicate the hazards and risks of the materials being transported to |
|
|
|
anyone who could be exposed to them. All markings must be legible and |
|
|
|
durable; clearly visible; written in English; printed on or affixed to the |
|
|
|
package surface or a label, tag, or sign; and placed away from other |
|
|
|
markings (such as advertising) that could substantially reduce their |
|
|
|
effectiveness. DOT marking requirements are detailed in Part 172, |
|
|
|
Subpart D of the HMR. |
|
|
|
At the end of this module, you will be able to: |
|
|
|
· Define the terms "hazardous material," "packaging," "package," |
|
|
|
"bulk packaging," and "non-bulk packaging," as defined in the |
|
|
|
Hazardous Material Regulations (HMR) |
|
|
|
· Identify the responsibilities of shippers, carriers, and drivers for |
|
|
|
hazardous material shipments |
|
|
|
· List general packaging requirements for hazardous materials |
|
|
|
· Identify UN POP marks, Box Maker's Certificates, and "Glass - |
|
|
|
Handle with care," "Keep dry," and "Upright position" markings |
|
|
|
· Identify general, material-specific, and packaging-specific marking |
|
|
|
requirements for bulk and non-bulk packaging |
|
|
|
· Identify the DOT markings used to identify marine pollutants, |
|
|
|
radioactive materials, poisons, self-reactive materials and organic |
|
|
|
peroxides, explosives, regulated medical waste, and elevated |
|
|
|
temperature materials |
|
|
Who can attend? |
|
|
|
Validation? |
Three years |
|
|
Certificate & ID |
Certificate & ID |
|
|
Exam |
Multi-choice exam |
|
|
Fee |
325 US$ + VAT |
|
|
More details |
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DOT Hazmat - |
The primary function of hazmat packaging is to ensure that hazardous |
|
|
Packaging |
materials remain intact and secure during transportation. All packagings |
|
|
|
must be designed to ensure that under normal conditions, the contents will |
|
|
|
not be released and the packaging effectiveness will be maintained as it |
|
|
|
experiences typical physical stresses, including shocks, vibrations, |
|
|
|
temperature extremes, and changes in humidity and pressure. The |
|
|
|
Hazardous Materials Table (HMT) in Section 172.101 of the HMR can be |
|
|
|
used to determine the non-bulk and bulk packaging requirements, and any |
|
|
|
conditions for packaging exceptions, for hazardous material shipments. |
|
|
|
At the end of this module, you will be able to: |
|
|
|
· Define the terms "hazardous material," "dangerous goods," |
|
|
|
"packaging," "package," "limited quantity," "excepted quantity," and |
|
|
|
"consumer commodity" |
|
|
|
· Identify when the Hazardous Materials Regulations, IMDG Code, |
|
|
|
IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations, and UN Recommendations |
|
|
|
apply |
|
|
|
· Demonstrate how to determine packaging exceptions and |
|
|
|
authorized packagings, and how to apply Special Provisions |
|
|
|
· Describe the purpose and application of DOT Special Permits |
|
|
|
· Show how Packing Group performance levels in UN POP marks are |
|
|
|
applied |
|
|
|
· List general HMR packaging requirements and common exceptions |
|
|
|
· Identify where the requirements for limited quantity and excepted |
|
|
|
quantity shipments can be found |
|
|
Who can attend? |
|
|
|
Validation? |
Three years |
|
|
Certificate & ID |
Certificate & ID |
|
|
Exam |
Multi-choice exam |
|
|
Fee |
325 US$ + VAT |
|
|
More details |
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DOT Hazmat - |
The DOT requires marking, labeling, and placarding of hazardous |
|
|
Placarding |
materials being transported in commerce to, from, or within the U.S. The |
|
|
|
term "placarding" refers to the placement of large durable versions of |
|
|
|
hazard labels on transport vehicles, bulk packages, freight containers, unit |
|
|
|
load devices, and rail cars. The purpose of marking, labeling, and |
|
|
|
placarding is to communicate the potential dangers of hazardous |
|
|
|
materials. Placards are especially important to emergency responders, |
|
|
|
who use this information to initiate protective actions after an incident or |
|
|
|
accidental release. |
|
|
|
At the end of this module, you will be able to: |
|
|
|
· Define the terms "hazardous material," "packaging," "package," |
|
|
|
"bulk" packaging, and "non-bulk" packaging, as defined in the |
|
|
|
Hazardous Material Regulations (HMR) |
|
|
|
· Identify the hazmat packaging employees who must comply with |
|
|
|
the HMR |
|
|
|
· Identify markings, labels, and placards on hazardous material |
|
|
|
shipments |
|
|
|
· Describe placards that are prohibited, including the exceptions |
|
|
|
that are allowed |
|
|
|
· Describe general placarding requirements for hazardous material |
|
|
|
shipments to, from, and within the U.S., including how to use the |
|
|
|
placarding tables in the HMR, and placarding provisions and |
|
|
|
exceptions |
|
|
Who can attend? |
|
|
|
Validation? |
Three years |
|
|
Certificate & ID |
Certificate & ID |
|
|
Exam |
Multi-choice exam |
|
|
Fee |
325 US$ + VAT |
|
|
More details |
|
|
|
|
|
|
DOT Hazmat - Security Requirements

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DOT Hazmat - Security |
In 2010, the Pipeline & Hazardous Materials Safety Administration |
|
|
Requirements |
(PHMSA) published a rule modifying the security requirements for the |
|
|
|
commercial transportation of some hazardous materials. This rule |
|
|
|
requires shippers and carriers of certain types and quantities of hazardous |
|
|
|
materials to implement a Hazardous Materials Safety and Security Plan |
|
|
|
(a.k.a. "Security Plan") and provide additional security training to |
|
|
|
employees. Among other things, they must ensure subject hazmat |
|
|
|
packages and containers are properly closed and secured, select routes |
|
|
|
that will minimize damage to or from hazardous materials, conduct |
|
|
|
background investigations on new employees, confirm the adequacy of |
|
|
|
carrier Security Plans, and integrate all aspects of the security rule into |
|
|
|
their normal business activities. |
|
|
|
At the end of this module, you will be able to: |
|
|
|
· Provide the Hazardous Materials Regulations (HMR) definition for |
|
|
|
"hazardous material" and "large bulk quantity" |
|
|
|
· Identify which shipments are subject to the HMR |
|
|
|
· List the required elements of a Hazardous Materials Security Plan |
|
|
|
· Describe the three types of security that a Security Plan must |
|
|
|
address: personnel security, unauthorized access, and route |
|
|
|
security |
|
|
|
· Describe the recordkeeping requirements for Security Plan |
|
|
|
documents |
|
|
|
· Describe the general training and in-depth security training |
|
|
|
requirements for hazmat employees |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Who can attend? |
|
|
|
Validation? |
Three years |
|
|
Certificate & ID |
Certificate & ID |
|
|
Exam |
Multi-choice exam |
|
|
Fee |
325 US$ + VAT |
|
|
More details |
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DOT Hazmat - Shipping |
Shippers of hazardous materials - including hazardous wastes, hazardous |
|
|
Papers |
substances, and marine pollutants - must prepare and certify shipping |
|
|
|
papers before offering these materials for commercial transportation to, |
|
|
|
from, or within the U.S. Shipping papers identify and classify the |
|
|
|
hazardous materials being shipped, and notify shippers and carriers of |
|
|
|
their hazards. They help define the protective measures necessary to |
|
|
|
protect employees, the public, and the environment, and can provide |
|
|
|
critical information to emergency response personnel. |
|
|
|
At the end of this module, you will be able to: |
|
|
|
· Describe the shipping paper preparation and recordkeeping |
|
|
|
responsibilities of shippers, drivers, and carriers |
|
|
|
· Identify the requirements for the Emergency Response Telephone |
|
|
|
Number on shipping papers |
|
|
|
· Describe common exceptions for shipping paper requirements |
|
|
|
· Identify the required components of a Basic Description and |
|
|
|
Proper Shipping Description |
|
|
|
· List the additional information that is required for some |
|
|
|
hazardous material shipments |
|
|
|
· Identify the four types of shipper certifications |
|
|
|
· List the additional information that is included on the Uniform |
|
|
|
Hazardous Waste Manifest |
|
|
Who can attend? |
|
|
|
Validation? |
Three years |
|
|
Certificate & ID |
Certificate & ID |
|
|
Exam |
Multi-choice exam |
|
|
Fee |
325 US$ + VAT |
|
|
More details |
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DOT HAZMAT Safety |
Over 4 billion tons of hazardous materials are transported in the U.S. |
|
|
|
every year. Due to their inherent risks to life, property, and the |
|
|
|
environment, the U.S. DOT established the Hazardous Materials |
|
|
|
Regulations (HMR) to cover the classification, labeling, packaging, and |
|
|
|
handling of hazardous materials. They also regulate hazmat training, |
|
|
|
incident reporting, hazard communication, and security. This course |
|
|
|
describes existing regulations for the transport of hazardous materials in |
|
|
|
commerce in the U.S., including the Hazardous Materials Table (HMT). |
|
|
|
At the end of this module, you will be able to: |
|
|
|
· Provide the U.S. Department of Transportation's (DOT) definitions |
|
|
|
for "hazardous material," "hazmat employer" and "hazmat |
|
|
|
employee" |
|
|
|
· Describe the key components of the U.S. DOT's Hazardous |
|
|
|
Materials Regulations (HMR) |
|
|
|
· Identify who must comply with the HMR |
|
|
|
· Use the information in the Hazardous Materials Table (HMT) from |
|
|
|
the HMR to correctly fill out the shipping description on a |
|
|
|
shipping document for a hazardous material |
|
|
|
· List the civil and criminal penalties that are possible for violations |
|
|
|
of the HMR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Who can attend? |
|
|
|
Validation? |
Three years |
|
|
Certificate & ID |
Certificate & ID |
|
|
Exam |
Multi-choice exam |
|
|
Fee |
325 US$ + VAT |
|
|
More details |
|
|
|
|
|
|

